Germany is a nation that elevates higher education to an exceptional level on the global stage. The majority of German universities offer top-notch scholarships to international students.
Numerous excellent English-taught programs are offered by German universities in a variety of specialties. Majority students have nothing but positive things to say about the academic staff and the services provided by German universities.
There are four main components of the education system in Germany: Kindergarten school, Grundschule, or primary school, secondary education which has 5 different stages, and lastly higher education. It is compulsory to enroll in schooling when a child is six years old in Germany. Most of the government-run schools run free of tuition fees.
Germany is among the top countries in terms of higher education. Moreover, each year it hits new records for international students who are mainly from Asia and Europe. There are many advantages of higher studies in Germany for students.
History of German Education
The development of formal and informal learning is covered by the history of education system in Germany. Officially, German public education was established back in the 18th century. The history of German education is very extensive and we have to look back to the 18th century to find it out.

establish free primary education. It was generally mandatory primary education in an eight-year program during the 18th century. The program gave detailed knowledge in ethics, duty, discipline. Additionally, it also taught children about the abilities required in the very early stage of the industrialized world. During that educational introduction, the main focus areas were reading, writing, and math. Those who were financially solvent they availed the private initial for the next four years.
In 1810, Prussia saw the need for state certification requirements for instructors. Additionally, the Abitur (a certification given in Germany at the completion of secondary school) was first offered in 1788 which was later in 1812 adopted by all secondary schools in Prussia.
The German Empire
The German educational system was more centrally controlled after the establishment of the German Empire in 1871. During that time, the first female secondary schools with separate enrollment were approved by the state authority. Likewise, in the late 18th century, many secondary schools were built.
In the last half of 18th century, authorities developed four different kinds of secondary schools:
Gymnasium: It is a nine-year classical program which has Latin, Classical Greek or Hebrew, as well as one modern language study. It is also available in today’s education in Germany with many changes.
Realgymnasium: It was also a nine-year program with Latin, contemporary languages, physics, and mathematics as the main subjects.
Realschule: It is a six-year program without a requirement for university admission but with the opportunity to train for modern industrial, office, or technical employment. It is also available in today’s education in Germany with many changes.
Oberrealschule: It is a program of nine years which focuses on modern languages, science and mathematics.
Weimar Republic
It is a four-year elementary school, called Grundschule, which is today;s elementary school. It was founded by the Weimar Republic after 1919. Almost every student continued their four-year education in those institutions.
Nazi German
The fundamental design of the educational system did not change during the Nazi era from 1933 to 1945. Even so, the curriculum was adjusted to teach the regime’s ideologies.
East Germany
During this era, the government gave education a high priority and made it mandatory for children starting at age six for a period of ten years. In the 1960s, the German Democratic Republic also known as East Germany.
West Germany
The authorities made sure Nazi ideology was removed from the curriculum during that period. West Germany’s new constitution, which was adopted in 1949 gave state governments’ control over education. Multi-state agreements guarantee the fixing of essential factors. According to that, from the age of six until the age of sixteen, all children must attend one sort of school.
Federal Republic of Germany
In the 1990s, the education system saw some drastic changes. Later, bilingual education in various topics, teaching methods, experiments, technological improvements and Internet connection in every school are some significant steps seen in 90s’ in Germany.
Later, education in Germany saw so many changes and developments in the education system.
The above mentioned are the evolution of the German Education System. Seeing the drastic development and the well structured initiatives regarding education you can understand why Germany’s Education is on top and people from all over the world choose Germany for their higher education destination.
Level of Education in Germany
There are four different stages in the education system in Germany. They are: Kindergarten school, Grundschule or primary school, secondary education which has 5 different stages and lastly the higher education.
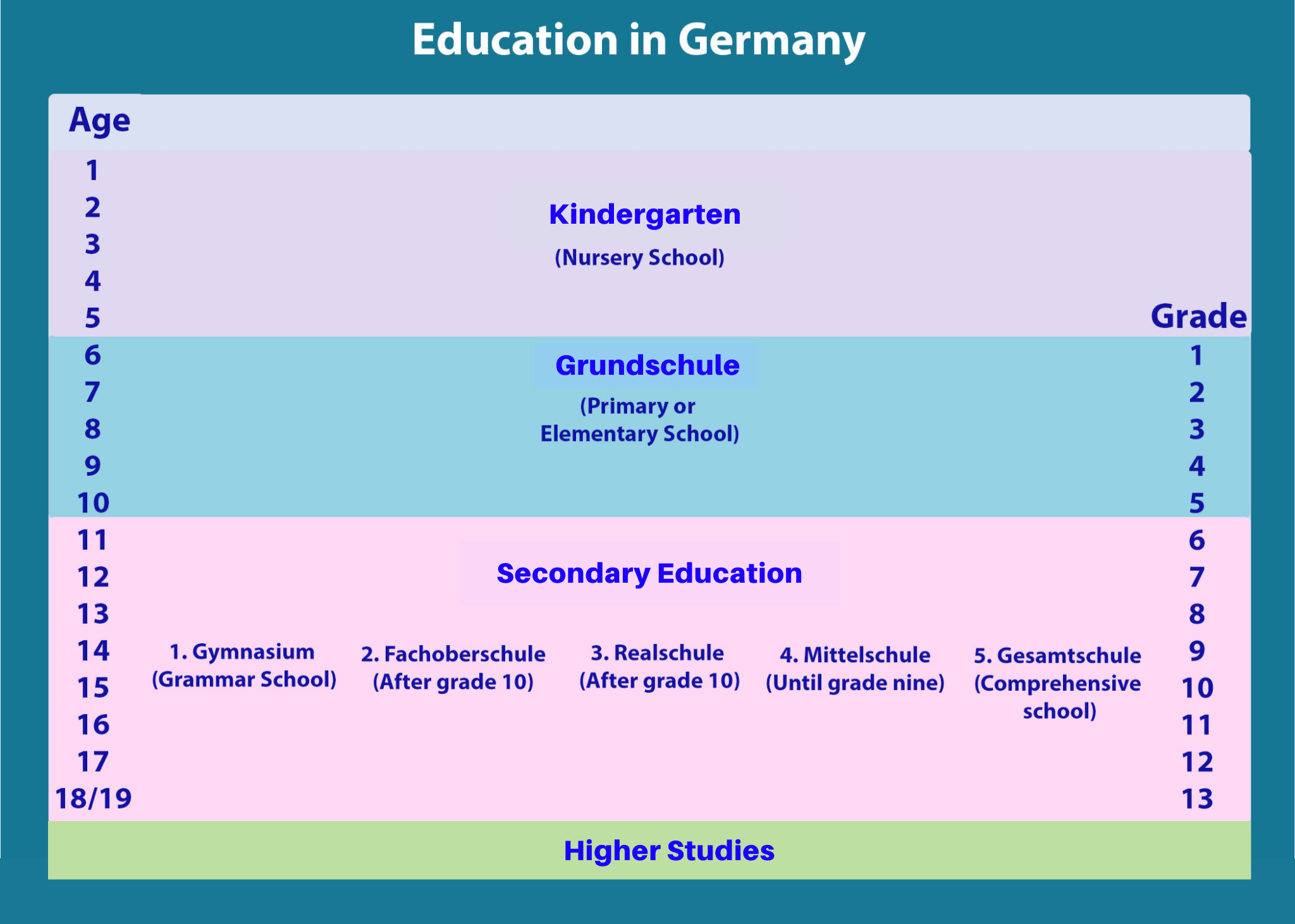
Kindergarten school
A kindergarten, or Kita, is a term used in German to address preschool for children. Kindergarten classes are not a part of the German education or schooling system. However, Kita is attended by children between the ages of 2 and 6.
Grundschule or Primary or Elementary School
The main focus of education system in Germany is on secondary education. Here, children were prepared for secondary schooling in Grundschule or elementary schools. Public schools in Germany do not take any fees from students. The majority of students attend neighborhood public schools. The entering year is ranged from 5 to 7 or moving up or down a grade based on students’ result and ability of understanding.
Secondary Education
The most important stage of a student’s life is secondary level of education system in Germany. From the development of education system in Germany, secondary schooling has been the most top priority. There are five sections in secondary schooling in Germany. They are:
Gymnasium: It is one of the oldest stages in the German education system. This stage is also known as grammar school. It is taught until grade 12 or 13 with Abitur, a certification given in Germany at the completion of secondary school.
Fachoberschule: It is an admission test after grade ten until grade twelve.
Realschule: It is taught until grade ten.
Mittelschule: It is the least academic, much like a modernized Volksschule elementary school until grade nine.
Gesamtschule: Ii is known as comprehensive schooling.
Higher Education
The last education stage for which Germany is worldwide famous, is higher education. German universities are recognized worldwide.
Germany’s postsecondary education system distinguishes between two types of institutions: Universitäts are the name for universities with the power to confer doctorates. Other degree-granting higher education institutions may be referred to by the more inclusive term Hochschule.
Most Popular Universities in Germany
Germany is home to 18 of the top 200 universities worldwide and six of the top 100. Moreover, in the QS World University Rankings, Germany always scores among the top 10. There are so many well reputed universities and education system in Germany is on high demand. The top universities in Germany are listed down below with the rankings:
University Names | Location | QS Ranking | Global Score |
Technical University of Munich | Munich | 49 (In 2023) | 76.4 (In 2023) |
Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich | Munich | 59 (In 2023) | 70.4 (In 2023) |
Heidelberg University | Heidelberg | =65 (In 2023) | 69 (In 2023) |
Humboldt University of Berlin | Berlin | =128 (In 2022) | 54.8 (In 2022) |
KIT, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology | Karlsruhe | 136 (In 2022) | 53.4 (In 2022) |
Freie Universität Berlin (Free University of Berlin) | Berlin | 127 (In 2022) | 54.9 (In 2022) |
RWTH Aachen University | Aachen | 165 (In 2022) | 48 (In 2022) |
Berlin Institute of Technology (Technische Universität Berlin) | Berlin | 159 (In 2022) | 49.3 (In 2022) |
Most popular programs in Germany
Popular programs | Course Duration | Available in | Approximate Cost |
Architecture | 4 Years 4 Years 3 Years | Technical University of Munich KIT, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology RWTH Aachen University | 4,454.85 USD per year 3,460 USD per year 2,867.04 USD per year |
Computer Science | 3 Years 3 Years | RWTH Aachen University Berlin Institute of Technology Technical University of Munich | 2,311.02 USD per year 2,961.81 USD per year 3,460 USD per year |
Medicine | 2 years 3 years | Technical University of Munich Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich | 3588.41 USD per year 3,183 USD per year |
Mathematics | 3 years 3 years 3 years | Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich Humboldt University of Berlin Free University of Berlin | 4,650 USD per year 5,637 USD per year 3,573 USD per year |
Law | 3 years 4 years 3 years | Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich Ruprecht Karl University of Heidelberg Humboldt University of Berlin | 4,354 USD per year 5,624 USD per year 4,670 USD per year |
Engineering | 4 Years 4 Years 3 Years | Technical University of Munich KIT, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology RWTH Aachen University | 4,353.85 USD per year 3,728 USD per year 2,625.04 USD per year |
Online Education in Germany
By 2021 and onwards, it was anticipated that Germany’s online education market would expand on a high note. Additionally, following the global Coronavirus outbreak, the number of online learning platforms increased dramatically in Germany.
There are now numerous platforms and applications available in the German online education market for all types of students. As a result, parents may now select the best platform based on their child’s learning requirements. The followings are the best distance learning institutions in Germany:
- FernUniversität Campus Hagen. Location: Hagen
- Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich. Location: Munich
- Heidelberg University. Location: Heidelberg
- Technische Universität München. Location: Munich
- IU International University of Applied Sciences. Location: Bad Honnef
- University of Freiburg. Location: Freiburg im Breisgau
- Eberhard Karls University of Tübingen. Location: Tübingen
- University of Göttingen. Location: Göttingen
- Best Areas for International Students in Germany
Numerous students from all around the world travel to Germany to study there. Germany is a diversified nation with everything from serene vineyards in the hills to top-notch cultural institutions in thriving cities. German cities are rich in history, fine art, and delicious cuisine, regardless of where you decide to study. The best places for International Students in Germany are listed down below:
- Munich.
- Frankfurt.
- Berlin.
- Hamburg.
- Aachen.
- Bonn.
- Dresden.
- Stuttgart.
Scholarships and funding for international students in Germany
Rising higher education in Germany is not free, despite the fact that the opportunity to study in Germany has the ability to transform your life. For postgraduate studies, international students have access to the majority of German scholarships. A scholarship that is entirely sponsored is offered. Given that those programs are lengthier, undergraduate scholarships are not offered as frequently.
In addition, the majority of the top institutions in the EU take part in the Erasmus program, with German universities taking part in a number of study programs supported by Erasmus Mundus and Erasmus+ scholarships. The grants will pay for basic living expenses, airfare, and enrollment.
Work Permit and Career Development
In Germany, there are many additional phases to the regulations governing work permits following graduation. You can directly apply for a post-graduation work permit (PGWP) after finishing your studies. After completing the education, one must use the (PGWP) program to apply for a work permit visa. You must be a skilled worker in Germany and have a strong enough profile to apply for permanent residency.
You are permitted to work part-time which is 20 hours in a week during your academic year and full-time which is 40 hours in a week as an international student in Germany.
FAQs
Which European nation is the cheapest for international students?
Among other European countries Italy, Germany and France are the cheapest. The cost of living is typically between 700 and 1,000 euros per month in Germany. The cost of living is typically between 700 and 1,100 euros a month in France. Costs of living on average range from 700 to 950 euros per month in Italy.
Which European country issues student visas quickly?
Germany, Ireland, and the United Kingdom are among the top European nations that give students’ visas on a quick note.
When does education become free in Germany?
Almost all German public elementary and pre-elementary schools are free.
Can a foreign child attend a German public school?
Every foreign student is welcomed to enroll in any elementary or secondary school in Germany.
Which nation has the best educational system?
The United States, the United Kingdom, and Germany are the top 3 nations with the strongest educational systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Germany is the perfect country to earn your degree while studying abroad because of its rich culture, delectable cuisine, beautiful architecture, and vibrant student scene! Learning the German language and gaining cultural insight are two benefits of studying there.
The prestige of German universities abroad and the generally high academic standards pleased students who studied there. Most importantly, the world is well aware of German prowess in higher education and research works.
Please read our post titled “Study in Germany with Scholarship” for more information. You are welcome to leave a comment below if you have any questions regarding the German educational system.











